

This state-of-the-art XPS instrument has a capability to analyze the very small area where the user is interested in and a large area of the uniform sample surface.
Equipped with a dual scanning X-ray source composed of the monochromatic Cr Kα (5.4 keV) and Al Kα (1.5 keV), the PHI Quantes is capable of obtaining secondary electron images (SXI) by scanning X-ray beam over the sample, which precisely allows to identify areas and/or points where you want to analyze. Enhanced SmartSoft-XPS can control the X-ray anode position and the motorized mechanical shutter, which allows rapid switching between the Cr Kα and the Al Kα. The switchover requires no adjustments, making it easy to measure the same areas or points with both the Cr Kα and the Al Kα.
Software control of the X-ray anode allows rapid switching between the Cr Kα and the Al Kα. The switchover requires no adjustments, making it easy to measure the same spot with both the Cr Kα and the Al Kα.
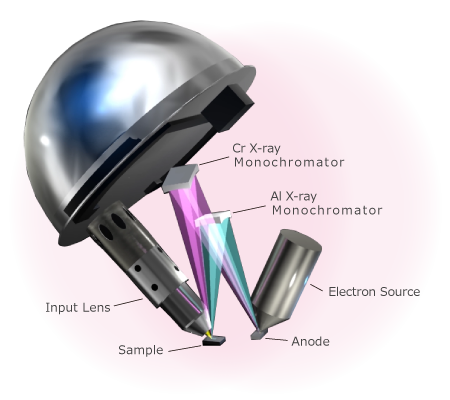 Schematic Diagram of Dual Scanning X-ray
Schematic Diagram of Dual Scanning X-ray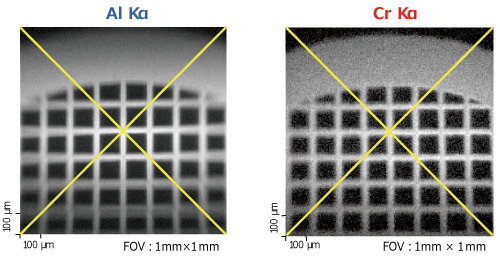 SXI Images with Dual Beam
SXI Images with Dual BeamThe patented turnkey charge neutralization that allows automatic charge compensation of the charged sample surface is also available on the PHI Quantes, as well as our other PHI XPS series, even when using Cr Kα.
> Description of Turnkey Charge Neutralization (to PHI Quantera II)
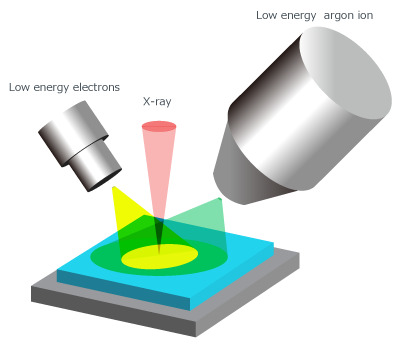 Schematic Diagram of Turnkey Charge Neutralization
Schematic Diagram of Turnkey Charge Neutralization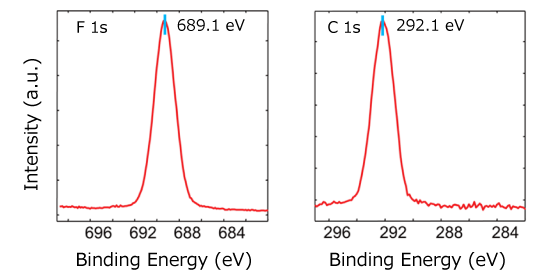 F 1s and C 1s Spectra of PTFE Measured using the Cr Kα
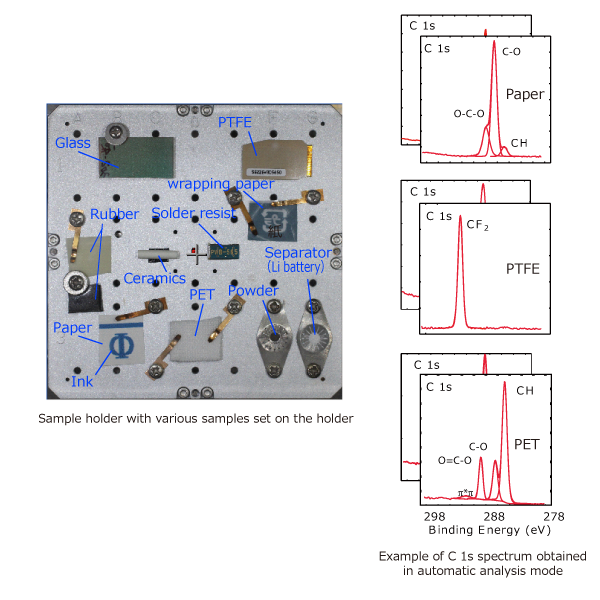
F 1s and C 1s Spectra of PTFE Measured using the Cr KαFully-automated analysis routine can be easily programed even if it takes days. The two standard parking positions in the analysis chamber enables fully-automated measurement of all samples, maximum of three, set on the PHI Quantes. In addition, the state-of-the-art turnkey charge neutralization technique also allows fully-automated analysis on insulating samples.
> Description of Navigation and Automatic Analysis (to PHI Quantera II)
The proven high voltage analyzer, together with the newly-developed high transmission input lens, on the PHI Quantes enables superior sensitivity even when using Cr Kα. High voltage proof 32-channel multi-channel detector allows snapshot acquisition up to 128 channels in interlaced mode.
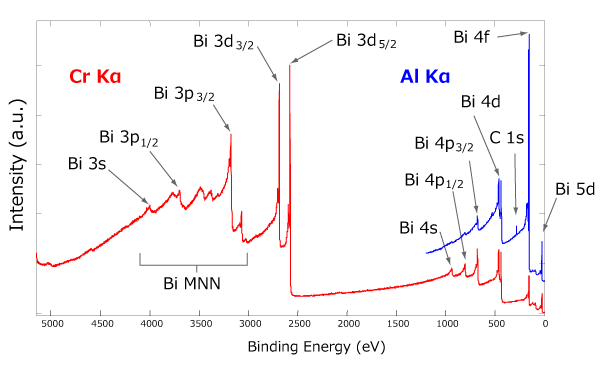 Survey Spectra of Cr Kα and Al Ka
Survey Spectra of Cr Kα and Al KaHere is an example of information from the Si substrate, obtained through PMMA films with different thicknesses, measured using the Al Kα and Cr Kα.
Information depth of using Cr Kα is about three times larger than Al Kα.
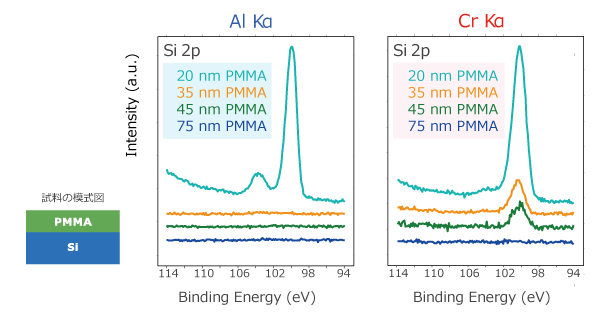 (Sample Provided by Fujifilm Corporation)Si 2p Spectrum from Si Substrate Detected through PMMA
(Sample Provided by Fujifilm Corporation)Si 2p Spectrum from Si Substrate Detected through PMMAData processing of the results of the Cr Kα can be performed in the same manner as the conventional XPS using the PHI MultiPak analysis software.
The MultiPak software also includes database of photoelectron peak positions (PeakID) and relative sensitivity factors (RSF) of elements, which are compatible with Cr Kα. RSF database for Cr Kα allows quantitative evaluations as well as Al Kα.
Spectra taken by Al Kα and Cr Kα can be processed simultaneously on the MultiPak, which allows simple comparison and other data processing between results of different X-ray source.
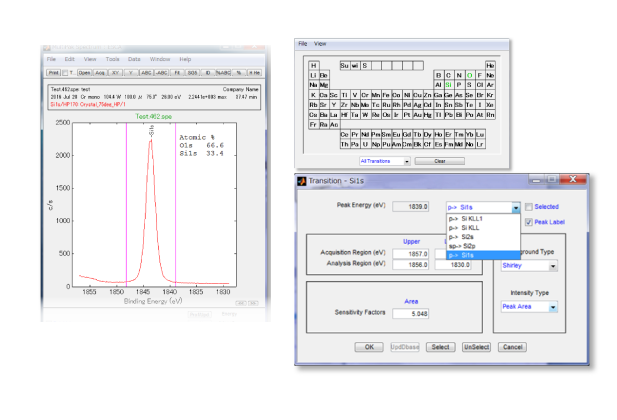 Example of Analysis Screen by PHI MultiPak
Example of Analysis Screen by PHI MultiPakWith this option on the Q series of automatic models, fully automatic measurement of the Dual X-ray x Dual Ion gun is now available.
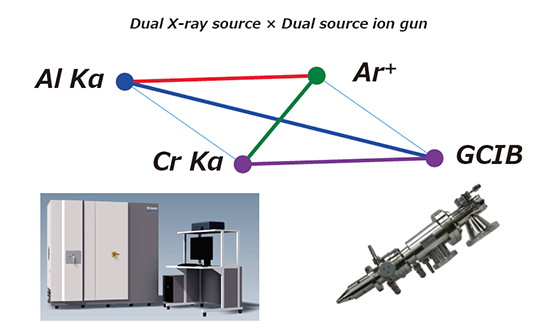
The Dual Ion Gun is a monomer/cluster switchable dual ion gun built into the vacuum chamber. It can be mounted in place of the standard built-in monomer ion gun and can be used for inorganic depth analysis using monomers and low-damage organic depth analysis using clusters with a single ion gun. Naturally, this ion gun is also capable of handling the low-acceleration ion in the neutralization mode, which is one of our unique reputations.
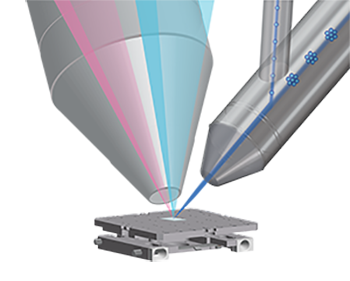
In addition, the new Dual Ion Guns can be used to change the cluster size, and a new cluster size instrument can be developed and added. This makes it possible to confirm the actual cluster size used inside the device.


OptiPMD determines the boiling range characteristics of petroleum products in less than 10 minutes, using only 10 ml of sample and it’s included in at least 10 fuel specifications.

The XM66 moisture analyzer offers the option to store four weighing results which make it possible to calculate the ash residue after ashing of the specimen has been completed externally.

The 6800-18 Aquatic Chamber is used to measure steady-state carbon assimilation and chlorophyll a fluorescence from an algal suspension using the LI-6800 Portable Photosynthesis System, the preferred photosynthesis system for terrestrial plant research.


The most advanced broad ion milling system for producing exceptionally high-quality cross-section or flat-milling samples for electron microscopy.
You may contact our specialists by accomplishing form below.
You may contact our specialists by accomplishing form below.